.jpg)
What Is Edge Computing? Everything You Need to Know
What Is Edge Computing? - Everything You Need to Know
With IoT becoming a crucial part of industrial and business operations, edge computing is garnering attention by helping enterprises take full advantage of their IoT solutions. Edge Computing aids business rise above challenges like latency, bandwidth, scalability, and security of IoT systems and devices.
Edge computing transforms how data generated through IoT and other devices get stored, processed, analyzed, and transported. It reduces the strain caused on traditional data center infrastructure by bringing processing power closer to the device that generates or consumes data.
With embedded hardware and software development exposure, eLogicTech Edge offers solutions that help reduce the challenges of connectivity, integration, control & management, as well as security & accessibility.


What Is an Edge Device and How Is It Related to IoT?
The devices using Edge computing, a distributed computing framework for locally collecting data and processing it while touching the physical environment, are called edge devices. They transmit data between the local network and the cloud server. Edge devices can translate between the protocols or languages used by the local devices, like Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, Zigbee, and NFC, into protocols used by the cloud, such as AMQP, MQTT, CoAP, and HTTP. Here, the edge device acts as a smart gateway in securely translating, sorting, and transferring information between the two sources. Without them, it would be difficult to transfer these data types of data to cloud services for deep analysis.


Edge Device Responsibilities and Sensor Interface
The responsibility of an edge device is to collect, process, and execute data in almost real-time with restricted help from other parts of the network. The sensors are connected to the edge device and equipped with a microprocessor unit to measure and generate data about physical phenomena.
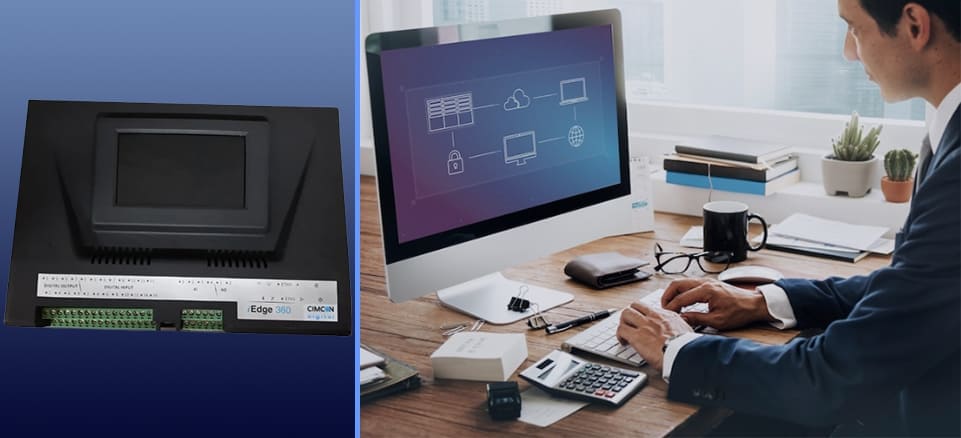
Intelligent edge terminals like CIMCON iEdge 360 provide multiple networks, including industry-standard communication networks, allowing existing and new sensors to connect to a single device. The edge device transforms data based on the use case and then sends raw and transformed data to the public or on an IoT platform for visualization and analytics based on the use case.

.jpg)
Identification of Opportunities
Industry 4.0 optimizes the daily operations of manufacturers with connected machines and data from sensors. The analysis of collected data identifies maintenance, performance, and other issues in a reasonable timeframe.
For example, connecting sensors to CNC machines help collect information on actual operating speed, run time, and performance parameters in real-time. The data gathered gets transmitted to the cloud for processing, triggering real-time analysis and developing informative insight about equipment utilization KPIs, such as TEEP, OEE, set up, and adjustment time. It helps reduction in machine downtime, fault prevention due to an early warning system, and continuous improvement of machines based on machine benchmarking and condition monitoring.
Optimization of Inventory Management and Supply Chain
For asset management, physical devices get installed with sensors and connected to the central monitoring system (CMS). These devices get a virtual IP address enabling them to communicate with central intelligence through IoT gateways and sensors. And then transmit asset-related information like existing location, running status, condition, and possible malfunctions to the CMS. The asset manager can take instant action on a particular asset for maintenance or any other work order.
IoT with RFID enables asset tracking. An asset labeled with an RFID tag gets a unique ID linked with asset data stored in the cloud, such as the asset’s physical parameters, cost, serial number, model, assigned employee, area of use, etc. And scanning the tag with an RFID reader scans and updates the data in the database


Predictive Maintenance and Analytics
IoT allows manufacturers to predict when a problem will occur without it happening.
EDM process data was earlier stored in a database and monitored once a day. The application of software connector-assisted reading and display of the data directly from the machine helped in the early detection of cycle time deviation. The team could evaluate the status and notify associates for checking and servicing of machines. The production output increased with predictive analytics.
A predictive maintenance system comprises IoT, cloud, mobile applications, AI/ML, and web applications to collect data, process the data, push notifications, analyze, predict insight and share operational data under one roof.

Fleet Management
Industry 4.0 has digitalized and automated the fleet management process with IoT. IoT-embedded system with key technologies like GPS, OBD, and RFID has improved vehicle routing and tracking, engine performance, fuel efficiency analysis, predictive fleet maintenance, etc. It is crucial to design embedded hardware customized to the users' requirements to meet the performance parameters.
The use of cargo camera sensors helps determine available space within a trailer remotely, and based on the data, dispatchers can link a truck to an optimal load. Integrating additional data, such as drivers' available working hours, local weather, and traffic data, can further help improve driver and asset utilization ratios.


Home Automation
The application of IoT helps control home appliances and thus automates modern homes through the internet, like lighting, kitchen, safety and security system, temperature control, and retro-fits. A smart home lighting system can change between warm and bright light with different color hues to suit our requirements and mood. Smart sensors can check for gas leaks, smoke, and water leakage and turn off the power in the house if indicators are out of range.
Technologies Pushing Different Sectors Toward Industry 4.0
Industries are using AR for maintenance, logistics, and all kinds of SOP, such as-display of supporting information through glasses. The cross-company data integration based on data transfers standards preconditions for a fully automated value chain from supplier to customer and management to shop floor. The industrial internet refers to the network of machines and products leading to multidirectional communication between networked objects.


Technologies Pushing Different Sectors Toward Industry 4.0

Industry 4.0 is the convergence and application of technologies, such as advanced robotics, additive manufacturing, AR, simulation, horizontal/vertical integration, industrial internet, cloud, cyber security, and big data and analytics.
Advanced robotics includes autonomous and cooperating industrial robots with numerous integrated sensors and standardized interfaces that help reduce human work. Additive manufacturing is 3D printing for spare parts and prototypes, facilitates decentralized 3D for inventory, and helps minimize transport distance.
Industries are using AR for maintenance, logistics, and all kinds of SOP, such as-display of supporting information through glasses. The cross-company data integration based on data transfers standards preconditions for a fully automated value chain from supplier to customer and management to shop floor. The industrial internet refers to the network of machines and products leading to multidirectional communication between networked objects.
